Energy materials
This page collects some ideas about energy materials relevant for studies using our techniques.
Scope: What are energy materials?
Research in energy materials aims "to address materials needs in future energy generation, transmission, utilisation, conservation and storage" (Hald 2006).
Energy generation includes the following subjects (potential for materials research indicated in sub-list), with some overlap:
- thermal generation based on fossil fuels (coal firing plants, natural gas turbine plants)
- largest source of electricity production at present and for the foreseeable future (cheap; abundant coal reserves for 200+ years)
- efficiency is limited by T, P limits due to materials
- research into heat resistant steels and nickel-based alloys aims to increase the current efficiency of ~45% to > 50%
- CO2 storage & sequestration aims to zero-emission coal-based energy production
- nuclear power
- research into new fission reactor designs (Wikipedia: Generation IV reactor designs) which also provide process heat for hydrogen cogeneration
- fusion reactor research: ITER project; the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility for testing candidate materials
- renewable energy and distributed power
- photovoltaics
- (see own section)
- fuel cells
- (see own section)
- wind power, wave power
- biofuels
- water splitting and photocatalysis
- photovoltaics
- the "hydrogen economy"
- hydrogen generation
- electrical-hydrogen cogeneration increases powerplant efficiency
- hydrogen distribution
- hydrogen storage
- liquid and solid state carriers
- fuel cells
- hydrogen generation
Energy storage includes batteries and hydrogen storage.
Research activity
Energy materials occupy a strongly growing share of materials science research. Two new journals have been recently introduced: Energy Materials in 2006 (not included in ISI), and Advanced Energy Materials in 2011. Adv. Energy Mater. is a branch of Adv. Mater. (impact factor 10.8 in 2010). The editorial of the first issue of Adv. Energy Mater. reports the following distribution of energy-related papers in Adv. Mater. (Ottmar2011)

Photovoltaics clearly dominate the number of energy-related publications in Adv. Mater. journals, followed by a large activity in batteries research. Fuel cells and hydrogen storage are less represented.
Relevant applications
Including references to potentially interesting work.
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV), i.e. solar cells.
Key issues: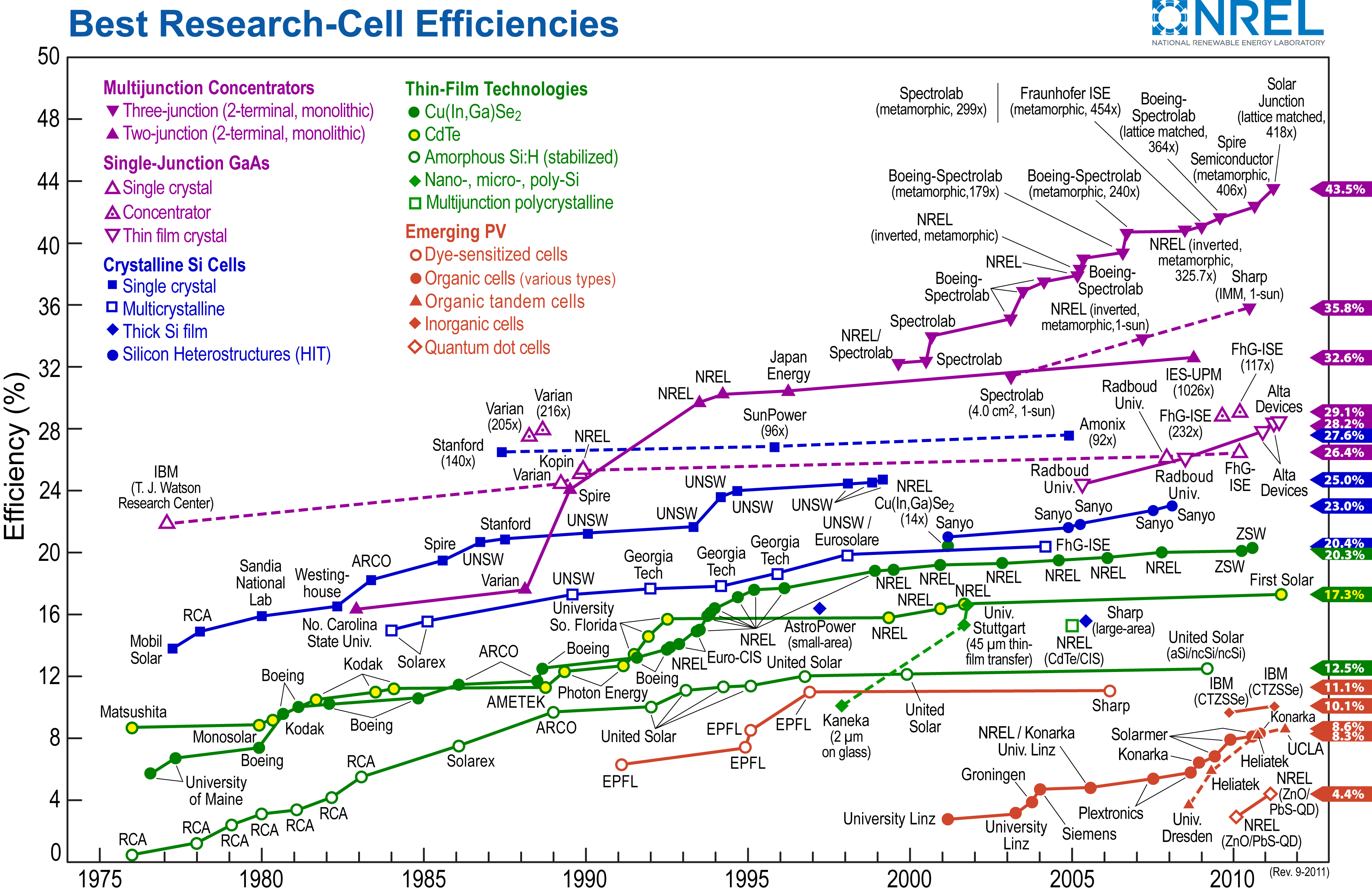
- manufacturing cost
- lifetime, degradation
- traditional solar cells are very efficient, organic cells still improving
Finnish research groups:
Organic solar cells
- molecular organic solar cells
- polymer solar cells
- Brabec et al. Plastic solar cells (http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1616-3028(200102)11:1<15::AID-ADFM15>3.0.CO;2-A). Adv. Functional Mater. (2001)
- thin film materials (sub-micron)
Multiband semiconductor solar cell materials
Dye-sensitized solar cells
- Grätzel. Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature (2001).
Fuel cells
Key issues
- "The proton-exchange membrane (PEM) is a central, and often performance-limiting, component of all-solid H2/O2 fuel cells." (Schmidt-Rohr 2008)
- "Understanding how PEM structure and morphology relate to mobile species transport presents a challenge for designing next-generation materials." (Li 2011)
Articles
- Li et al. Linear coupling of alignment with transport in a polymer electrolyte membrane. Nature Mater. (2011).
- Schmidt-Rohr & Chen. Parallel cylindrical water nanochannels in Nafion fuel-cell membranes. Nature Mater. (2008).
Arto's list of solid oxide fuel cell links:
- A. Jacobson. Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Chem. Mater. (2010).
- Braun et al. Molecular speciation of sulfur in solid oxide fuel cell anodes with X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Power Sources (2008).
- Ginestra et al. Characterization of nanoscale electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cell membranes. Presentation (pdf).
- Fuoss. Synchrotron x-ray studies of solid oxide fuel cell materials. Presentation (pdf).
- National Energy Technology Laboratory's fuel cell page
- Goodenough. Ceramic technology: Oxide-ion conductors by design. Nature (2000).
Batteries
Batteries and supercapacitors.
Key issues:
- energy density (Wh/kg) vs. gasoline
- cost
Articles:
- XRS measurement: Karan et al. Bulk-Sensitive Characterization of the Discharged Products in Li–O2 Batteries by Nonresonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C (2012)
- XRS measurement: Fister et al. Electronic structure of lithium battery interphase compounds: Comparison between inelastic x-ray scattering measurements and theory. J. Chem. Phys. (2011).
- Bruce et al. Li-O2 and Li-S batteries with high energy storage. Nature Materials (2012).
- Morita et al. Organic tailored batteries materials using stable open-shell molecules with degenerate frontier orbitals. Nature Materials (2011).
- Girishkumar et al. Lithium−Air Battery: Promise and Challenges. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. (2010).
- Duduta et al. Semi-Solid Lithium Rechargeable Flow Battery. Adv. Energy Mater. (2011). Local copy: . See article in MITnews: New battery design could give electric vehicles a jolt.
- Technology Review: Betting on a metal-air battery breakthrough.
- Defect concentration determination in novel lithium-iron-phosphate batteries (Press release)
- Lithium-iron-phosphate battery research at Aalto University
Some work involving CDC materials:
- Chimiola et al. Monolithic Carbide-Derived Carbon Films for Micro-Supercapacitors. Science (2010).
- Oschatz et al. A cubic ordered, mesoporous carbide-derived carbon for gas and energy storage applications. Carbon (2010).
- Dash et al. Titanium carbide derived nanoporous carbon for energy-related applications. Carbon (2006).
- Rose et al. Hierarchical Micro- and Mesoporous Carbide-Derived Carbon as a High-Performance Electrode Material in Supercapacitors. Small (2011).
- Magasinski et al. High-performance lithium-ion anodes using a hierarchical bottom-up approach. Nature Mater. (2010).
Hydrogen storage
- XRS measurement: Miedema et al. In situ X-ray Raman spectroscopy of LiBH4. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. (2012).
- Nature news feature: Hydrogen vehicles: Fuel of the future? Nature (2010).
CDC-related:
- Gogotsi et al. Tailoring of Nanoscale Porosity in Carbide-Derived Carbons for Hydrogen Storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2005).
Computational studies:
- Sigal et al. Is Hydrogen Storage Possible in Metal-Doped Graphite 2D Systems in Conditions Found on Earth?. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2011)
- Araujo et al. Thermodynamic analysis of hydrogen sorption reactions in Li–Mg–N–H systems, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 021907 (2008); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2830703
- Araujo et al. On the structural and energetic properties of the hydrogen absorber Li2Mg(NH)2, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 091924 (2007); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2775803
Fusion reactor materials
Chemical imaging of irradiation-induced defects?
Interesting materials
Carbide-derived carbon (CDC)
CDC, i.e. tunable nanoporous carbon, has many applications esp. in batteries and hydrogen storage.
It is well suited for x-ray studies (quite radiation resistant).
- Presser et al. Carbide-Derived Carbons – From Porous Networks to Nanotubes and Graphene. Adv. Functional Mater. (2011).
References
- J. Hald et al., Energy drivers for materials research and development. Editorial of Energy Materials, vol. 1, p. 1 (2006).
- M. Ottmar. A new journal sees the light (and other forms of energy). Editorial for Advanced Energy Materials, vol. 1, p. 8. (2011)
- Publication list of G. Yushin's group (Nanotech lab, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology): nanostructured materials for supercapacitors, fuel cells and batteries